
Beyond ChatGPT: How to Maximize the Use of ChatGPT with Interactive Graph Models

In just a matter of a year, ChatGPT has taken the world by storm, ushering in a new era of AI transformation. Its remarkable text-to-text generation capabilities have set new standards for informative and high-quality responses. Knowledge creation AI models like ChatGPT excel at engaging in conversations and retrieving information from vast databases. However, while it produces accurate and diverse answers, the delivery in text format can sometimes be hard to resonate with and fall short of user expectations. What if ChatGPT could also be used in combination with interactive visual representations? In this article, we delve into a method that combines the power of ChatGPT with interactive graph models, elevating the user experience to new heights.
The Role of Graph Data Modeling
A graph is a data structure that mirrors the natural interconnectedness found in the real world, enabling it to offer not just the desired information but also to suggest and provide additional, related data and information.

Learn more about the mechanics of Graph Databases->
The intricacies of Input Text & Output Text
To maximize the potential of ChatGPT, we must extend our goal beyond relying solely on existing text data and embrace the inclusion of "unstructured" information like images in the knowledge generation process. ChatGPT excels at delivering accurate answers, but achieving this precision often demands intricate and nuanced text prompts. Navigation and instruction of ChatGPT could often be challenging without guidance in the input text methods. In this regard, it is imperative to harness GPT's versatility by tapping into a variety of information sources, encompassing images. For instance, by introducing the user's hyper-personalized attributes in a simple user interface, the accuracy and relevance of information can be tailored to individual users.
To extend the information output from ChatGPT meaningfully, the specific information that the user needs must be identified from the collected pieces of information derived. In reality, however, GPT offers multifaceted textual information, which can be overwhelming for users seeking value within its output. To address this challenge, transforming the information produced by GPT into a 'knowledge graph' becomes a valuable approach. By mapping the connections between data points output by GPT onto a graph, it becomes feasible to visualize and index the desired information, uncover additional insights, and streamline GPT's knowledge management.

Creation and management of GPT knowledge using image information and graphs
Beyond obtaining information through 'text-to-text', let's elucidate on how to easily manage knowledge in the form of a graph by inputting images as a service using an example prompt, 'Generate Food Recipes from the Fridge.
In today's fast-paced world, many individuals have encountered the predicament of having to prepare a meal when faced with limited ingredients. Furthermore, tailoring a dish to one's specific dietary needs and personal preferences can be challenging. Let's tackle this by leveraging ChatGPT's capabilities along with the knowledge graph framework, empowering users to access top-tier insights with the simplest of inputs.
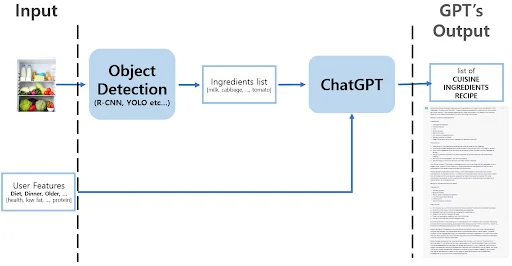
The above two models are used for extracting food recipes and information from the images of the ingredients in the fridge. As a first prompt, using object detection algorithms such as R-CNN or YOLO models, the ingredients present in the fridge are extracted. As for the second input value, it pertains to the user's unique preferences. To ensure accurate prompts, predefined options such as select boxes or radio buttons are employed.
In this workflow, both the ingredient list and the user's preferences are integrated into the ChatGPT prompt using a standardized format. Subsequently, GPT employs this data to craft a text output encompassing potential dishes, ingredients, recipes, and nutritional insights tailored to the user's specific traits, including factors like appetite, age, and time zone. This meticulous prompt engineering, which leverages both images and user characteristics, yields high-quality information to enhance the overall user experience.
Knowledge management using Graphs
When you input ingredients and user preferences into ChatGPT, the generated output comprises a 'dish,' 'recipe,' available ingredients, and additional ingredients suitable for the user. In Figure 4. below, by entering items like cabbage, tomato, and seaweed in your pantry, along with dinner preferences, dietary requirements, and age, GPT generates results related to 'cooking' and 'nutritional ingredients' as illustrated. This information is easily visualized through graphs and can be extracted into actionable knowledge.

Given that actual GPT information often spans over 70 lines of text, comprehending the desired details and their relationships can be challenging. Utilizing a graphical representation, you can observe that 'cabbage salad' was suggested as a recommended dish, along with 'salt and pepper' as essential cooking ingredients. Furthermore, dietary insights like 'dietary fiber' and 'digestion' were provided for users in the 'elderly' age group.
By leveraging these complex information interconnections, users can extract knowledge from GPT-generated data and discern common patterns among essential information elements.
This graph model can further be advanced into meal planning recommendations using the ingredients or nutrients in the food information. For example, by clicking on the 'cabbage, and 'tomato' nodes of an ingredient and putting them back into the GPT input prompt, it returns a dish that can be made with those ingredients, such as 'tomato-cabbage stir-fry'. If one clicks on the 'dietary fiber' and 'digestion' nodes in the nutrition component, 'older' and 'diet' are the most relevant characteristics through the edge search of the graph, leading to the 'seaweed soup' as a recommended dish.
This way, knowledge management using graphs enables users to secure visibility and identity and explore relationships between information to identify causality and relevance. A simple graph-type UI/UX also helps improve the productivity of ChatGPT by clicking on the appropriate node providing a data environment in a simple form that allows other food recommendations without having to separate prompt engineering.
Bringing the utilization of ChatGPT to the next level
ChatGPT holds significant promise for seamless integration with other models and efficient knowledge management. With a broader data spectrum and user-friendly graph-based knowledge management, it unlocks new insights and expands effortlessly across various domains. In particular, Apache AGE makes it easy to search and extract various knowledge by storing data in a graph. Being an extension to PostgreSQL, AGE allows a hybrid approach to databases combining the capabilities of both relational and graph queries, making it straightforward for beginners to view, extract, and manage graph information. Leveraging Apache AGE, the multi-database management system for generative AI knowledge, provides a low-barrier, versatile solution for making the most of this new era in knowledge management.
At AGEDB, we support the operation of Apache AGE to maximize its utility. Contact us now to get started or to learn more about adding graph models to your solution and services.