
Combating cyber attack with Apache AGE's link analysis.

Cybersecurity Background
In today's world, the internet has transformed how we connect, work, and access information, bringing unparalleled convenience and connectivity. This digital revolution, however, has its challenges, especially in cybersecurity. As we depend more on technology, the need to protect sensitive data and counteract cyber threats becomes increasingly critical.
Cybersecurity is about safeguarding our computer systems, networks, and data from theft, damage, or unauthorized access. A key part of this field is network intrusion detection. It's like a digital watchdog, constantly monitoring network traffic for any signs of suspicious activities, such as hacking attempts or unauthorized entries. The aim is to catch and address these threats early, preventing any harm to our networks or data.
In essence, cybersecurity and network intrusion detection are vital in our tech-driven world, ensuring our digital safety and resilience against ever-evolving cyber threats.
Data Overview
In the realm of cybersecurity, graph analysis plays a crucial role. To illustrate this, we use the CIDDS-001 dataset, specifically designed for network intrusion detection. This dataset serves as a benchmark for evaluating how different intrusion detection systems perform in identifying network attacks. It simulates a small business environment, complete with clients and servers, like email and web servers. The behaviors on these clients are mimicked using Python scripts, and the dataset includes unidirectional NetFlow data, capturing the flow of network traffic.
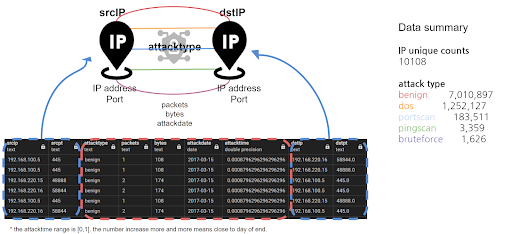
Figure1. Graph Modeling
Graph analysis in cybersecurity involves transforming relational data into a graph format, consisting of nodes (points) and edges (connections). There are two main types of graphs:
-
Homogeneous Graphs: These have nodes and edges of a single type, similar to what you'd find in social networks with user nodes connected by 'follow' edges.
-
Heterogeneous Graphs: These contain multiple types of nodes and edges, like in e-commerce networks where interactions between users and items are tracked through different types of connections such as 'buy,' 'cart,' and 'view.'
Using the CIDDS-001 dataset , we create a graph for network flow analysis. This includes nodes representing start and end points in the network, and edges of various types like 'benign,' 'dos,' 'portscan,' 'pingscan,' and 'bruteforce.' A key feature of this graph is the detailed information attached to each node and edge, such as ports, packet sizes, and timestamps. This level of detail is particularly valuable in cybersecurity, where quick and precise responses are crucial.
Cypher Query with Analysis Scenario
In this section, we explore how the PostgreSQL extension Apache AGE's graph analysis capabilities, particularly through Cypher queries, can be leveraged in cybersecurity. We'll look at three different scenarios, each demonstrating the power and flexibility of Cypher queries in analyzing network data.
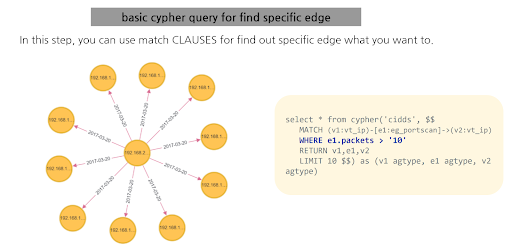
Figure2. Graph Query with Condition
Figure 2 showcases a Cypher query that focuses on identifying network packets larger than a certain size. This is a prime example of the 'condition' function in Apache AGE, which is crucial for pinpointing specific scenarios. Here, the query filters out packets larger than 10 units, helping analysts spot potential anomalies or threats in network traffic. This function isn't limited to just packet size; it can be tailored to various criteria, making it a versatile tool for cybersecurity analysis.
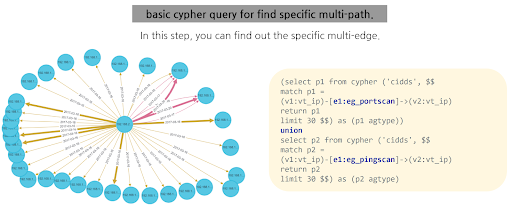
Figure3. Multi-path Search with Union Query
In Figure 3, we see a union query in Apache AGE, demonstrating its ability to handle complex, multi-path searches. This is particularly useful in scenarios where you need to analyze data across different types of connections, like 'eg_portscan' and 'eg_pingscan.' Apache AGE also enhances this analysis with visual aids, like representing the weight of packets through the thickness of edges in the graph, making it easier to interpret the data visually.
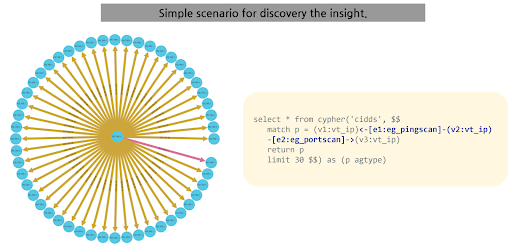
Figure4. Bi-directional Path Search
The final example, illustrated in Figure 4, is a bi-directional path search. This Cypher query uncovers one-to-many relationships between nodes, providing a detailed view of network interactions and potential security incidents. It's particularly adept at revealing complex patterns and relationships that might be missed with traditional analysis methods. By tracing paths involving different types of nodes and connections, this query helps in identifying multi-step attack patterns and potential sources or targets of cyberattacks.
In summary, these scenarios highlight the strength of Apache AGE in cybersecurity. Through its advanced graph analysis capabilities, Apache AGE enables cybersecurity professionals to uncover deep insights into network activities, detect threats more effectively, and enhance the overall security of network infrastructures.
Conclusion
Throughout this discussion, we've delved into the essentials of cybersecurity, examined the CIDDS-001 dataset for cyber intrusion analysis, and explored the dynamic use of Cypher queries in data analysis. The journey underscores the immense value of graph analysis in cybersecurity, offering profound insights and robust tools to combat digital threats.
Apache AGE stands out in this landscape, particularly for its user-friendly approach to graph analysis. The use of Cypher queries, known for their power and intuitiveness, simplifies complex data analysis. This language enables cybersecurity experts to craft detailed queries, uncovering complex attack patterns and suspicious network activities. Such flexibility is crucial in enhancing threat detection and response capabilities.
Graph visualization emerges as a key player in making intricate cybersecurity data more understandable and actionable. By graphically representing network nodes, edges, and their attributes, it becomes easier for analysts to decode complex structures, spot anomalies, and respond swiftly to potential threats. This visual approach aids in proactive security measures, allowing teams to trace unusual activities, map out attack routes, and pinpoint potential sources of cyber threats, thereby improving overall security awareness and decision-making.
Another significant aspect of Apache AGE's graph analysis is the labeled property graph model. This approach enriches nodes and edges with detailed metadata, capturing essential information about cyber incidents. Such rich data representation not only aids in precise threat categorization but also supports thorough post-incident analysis. This helps organizations learn from past experiences, enhancing their defensive strategies against future cyber threats.
In conclusion, Apache AGE presents a powerful suite of tools for cybersecurity professionals, significantly bolstering their ability to detect, investigate, and neutralize cyber threats. The combination of easy-to-use Cypher queries and effective graph visualization positions Apache AGE as an indispensable asset in contemporary cybersecurity operations. By adopting graph analysis, organizations can effectively stay ahead of cyber adversaries, protect sensitive data, and maintain the integrity of their digital ecosystems.